UTI Treatment

Dr. Arthur Tseng
Obstetrician & Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist at Gleneagles Medical Centre.
Book consultation!
We strive to help you manage urogynaecologic symptoms so you can get back to living your best life. Book consultation with Dr Arthur Tseng now!
Urinary tract infections can be an inconvenience, causing discomfort and incapacitation in women. UTIs are bacterial infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. If left untreated or if the initial UTI treatment was not sufficient, there is a risk of developing a complicated UTI which can lead to more severe infections such as kidney infection or kidney stones.
UTIs are especially common in females, requiring over six million visits to physicians per year in the United States alone. UTI refers to a bacterial infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
What is Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection?
Unfortunately, one in four (25%) women with a UTI is likely to develop a recurrent UTI. This means that they will have two or more episode of UTI within six months of their first infection. There are various risk factors for developing a recurrent UTI, including frequent sexual intercourse, pelvic organ prolapse, and a weakened immune system.
Signs and Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection
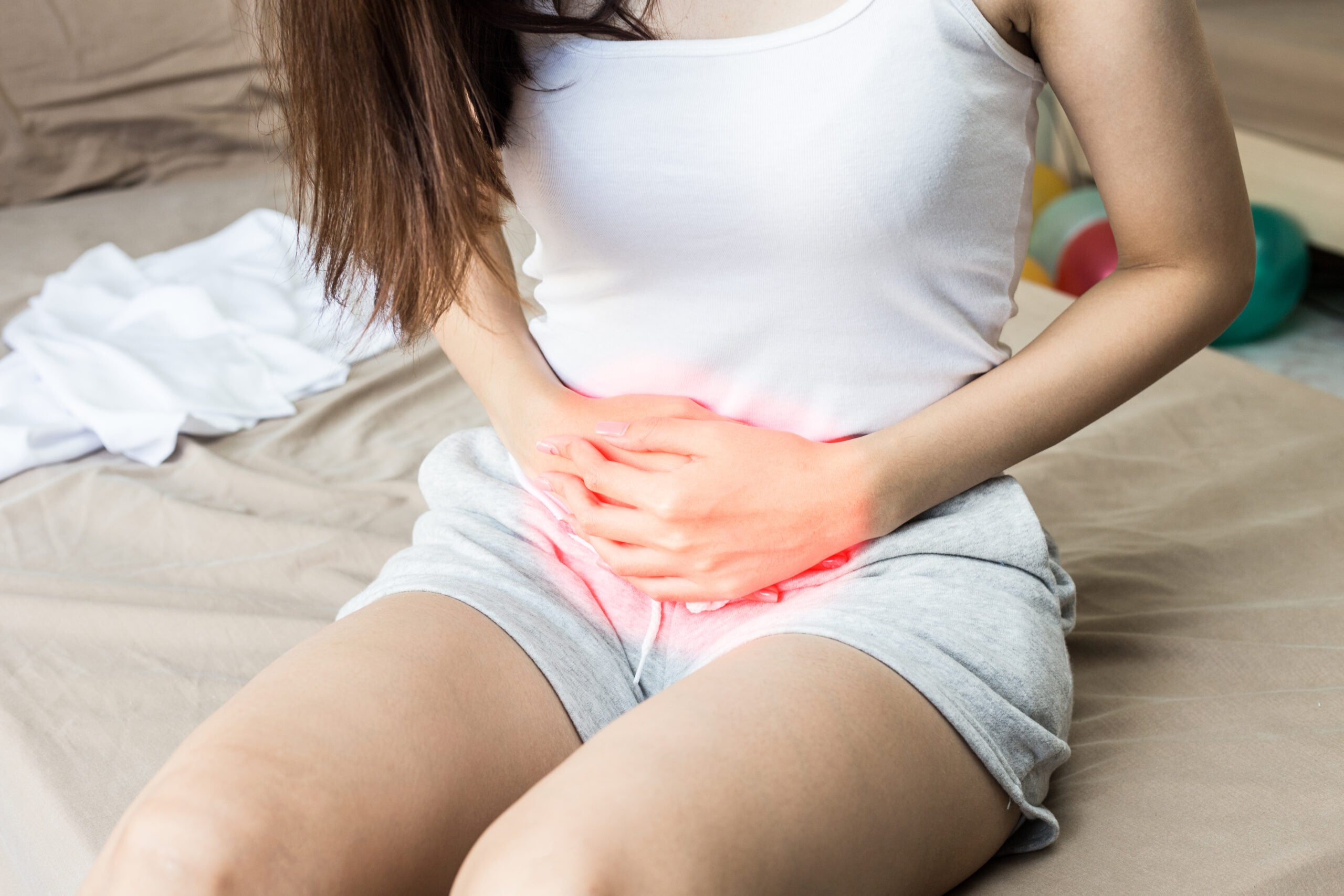

The symptoms of UTI can vary depending on the type of UTI, but common signs and symptoms include:
Burning sensation when urinating
Urinary frequency and urgency
Cloudy or bloody urine
Pelvic pain in Women / Rectal pain in Men
Foul-smelling and/or bloody urine
Voiding difficulties
If left untreated, a bladder infection can spread to the kidneys and cause more severe symptoms, such as fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and back pain. In these cases, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosing UTI
The diagnostic tools for UTI include urine tests, imaging studies, and other laboratory tests. Urine tests can detect the presence of bacteria in the urine, as well as white blood cells or red blood cells that may indicate infection. Imaging studies, such as a CT scan or ultrasound, can also reveal any abnormalities in the urinary tract. Finally, laboratory tests may be used to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and determine which antibiotics are most effective in treating it. The results of these tests help doctors diagnose UTIs accurately and determine an appropriate course of treatment.
UTI Treatment
The most common treatment option for UTI is antibiotics. Your doctor may prescribe a single dose of an antibiotic or short-term antibiotics, depending on the severity of your infection and any other existing medical conditions.
Other forms of treatment include drinking plenty of fluids to flush out bacteria or taking anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove a urinary stone or an obstruction causing blockage of the urinary tract.
It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully when taking antibiotics and other medications, as improper treatment can lead to a more serious infection.
Additionally, it is essential to practice good hygiene and drink plenty of fluids in order to prevent further infections. In some cases, lifestyle changes may be recommended to reduce the risk of recurring UTIs. This includes drinking lots of water, urinating frequently, wearing cotton underwear, avoiding douches or scented body washes, and wiping from front to back after using the bathroom.
Preventing UTIs
UTIs can be prevented by adopting healthy habits and taking precautions. This includes:
- Drinking plenty of water throughout the day to flush out bacteria from your urinary system.
- Emptying your bladder frequently, especially after sexual intercourse.
- Wiping from front to back after using the bathroom to prevent bacteria from entering the urethra.
- Avoiding harsh feminine products and wearing cotton underwear to keep the genital area dry and prevent bacterial growth.
It is important to seek medical advice as soon as you suspect that you may have a UTI in order to receive proper treatment and prevent serious complications. Contact your healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms of a UTI, such as burning or pain when urinating, frequent urge to urinate, fever, chills, and abdominal pain. Early UTI treatment can prevent the condition from worsening or resulting in serious infections.
Conclusion
Hence, there is a need to educate our patients on good hygiene habits. We should also consider the possibility of instituting non-antibiotic modalities of treatment and novel therapeutic methods that are on the horizon.
As we continue to learn more about this common infection, it is crucial to stay informed and consult with healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment. Together, we can work towards preventing UTIs and promoting overall urinary health. Early detection and proper treatment are key in managing UTIs and preventing them from becoming complicated. Let’s take care of our urinary system and prioritise our health!
DO YOU NEED TO MAKE
AN ENQUIRY?
Dr Tseng's expertise covers urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse, apart from that, his particular interest lies in the holistic management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome and other functional bladder conditions. With many years of experience in this field, he is committed to providing patients